Galaxies
Galaxies
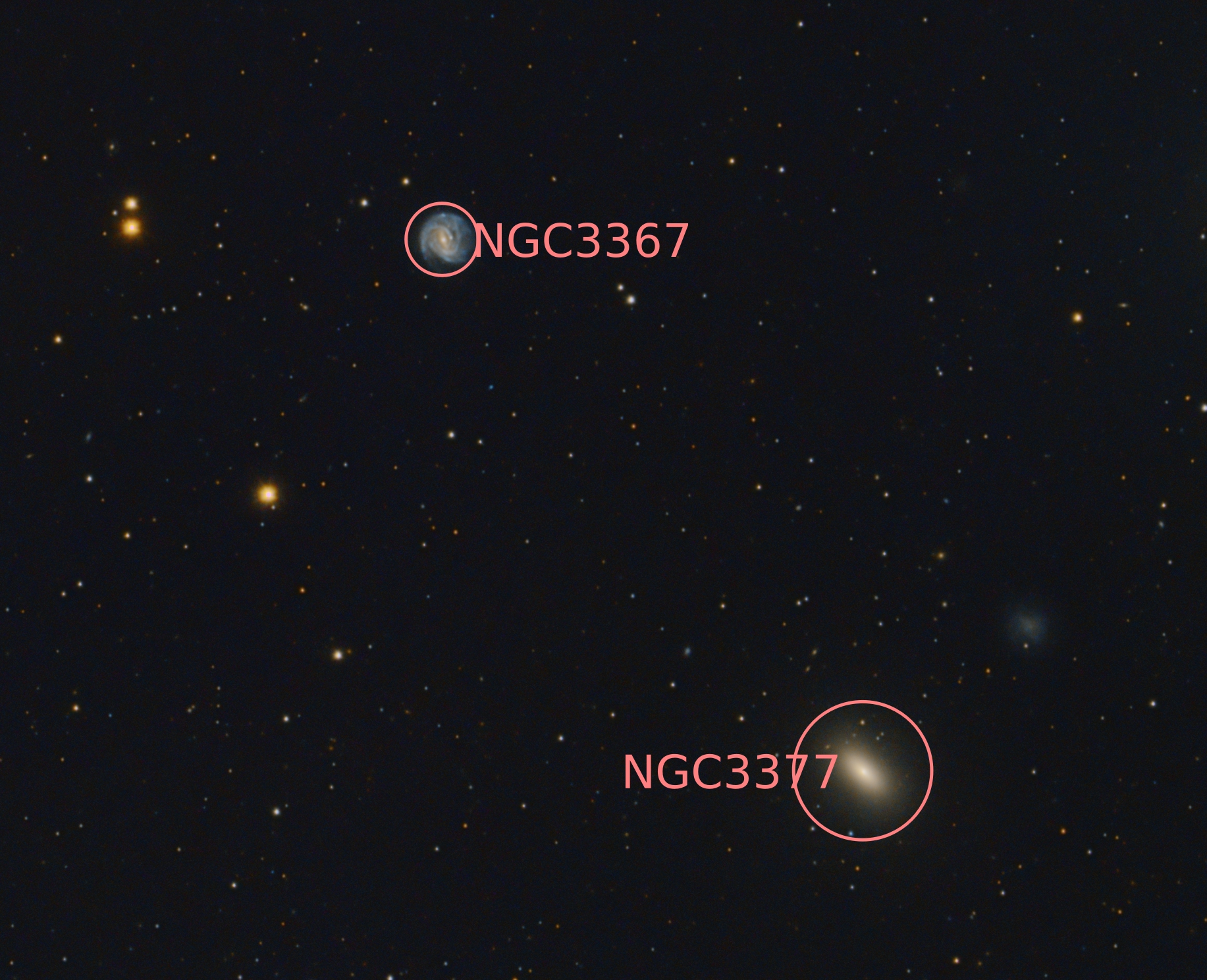
SN2022ewj, NGC 3367
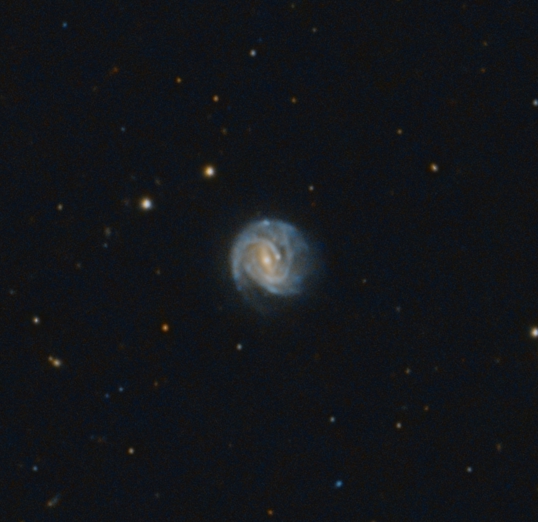

Another supernova currently visible in the northern hemisphere.
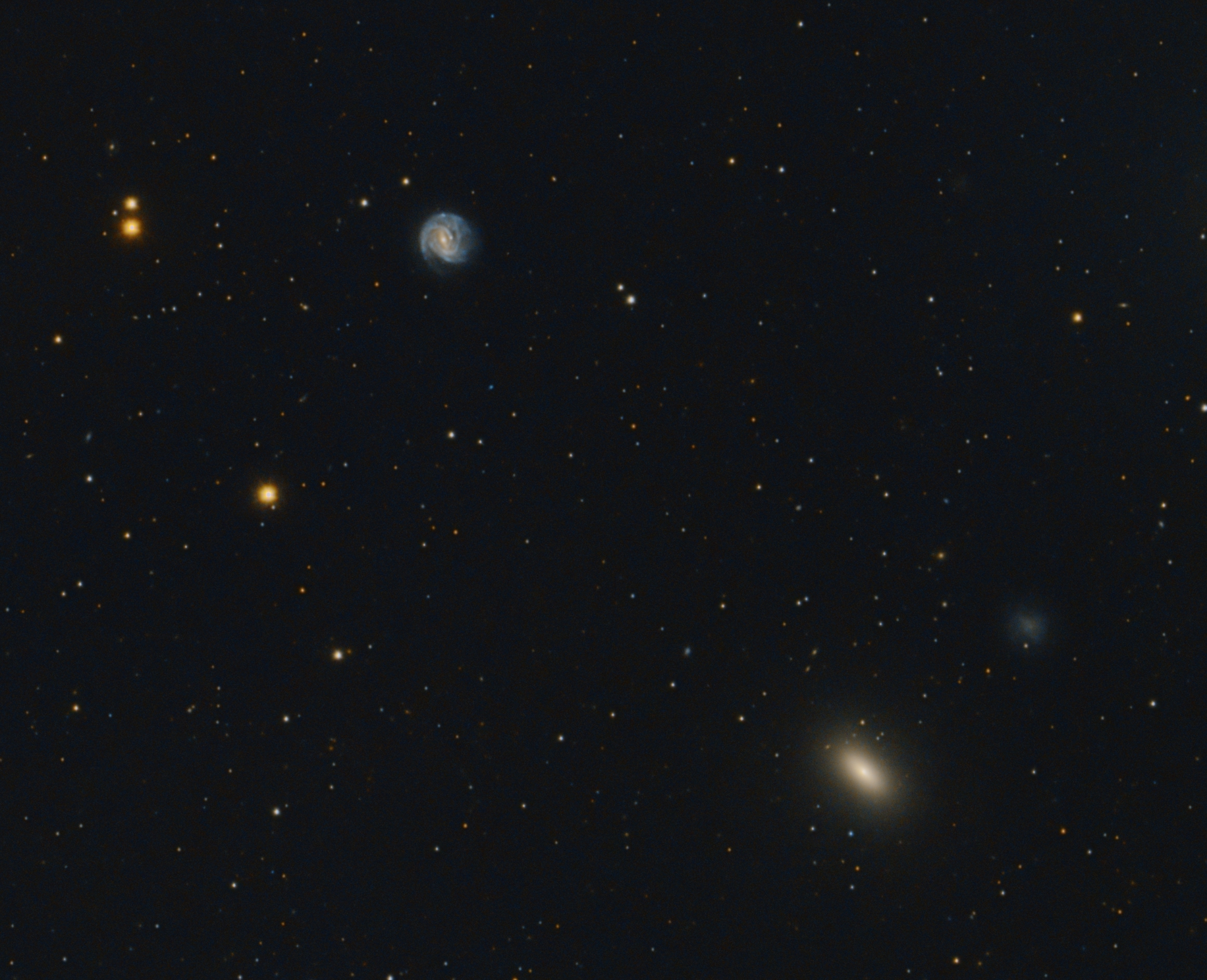
It has been discovered on 19th of March this year. It is located in this image at almost 3 o‘clock from the center of galaxy NGC 3367.
NGC 3367 is a barred spiral galaxy in constellation Leo approximately 130 million light years from earth. It has an active nucleus with a radio jet and is classified as a Seyfert Type 2 galaxy.
The supernova is of type II showing strong hydrogen lines in its emission spectrum. This kind of supernova has as its progenitor a star of at least 8 times the mass of the sun. Towards the end of the life time of such a giant star fusion reactions can build up elements up to iron. Fusing iron to even heavier elements would not release energy, so the iron simply accumulates in the core. The electron degeneracy pressure (a quantum phenomenon) in the core withstands gravity until the core reaches about 1.4 times the mass of our sun. Once this limit is reached (Chandrasekhar limit) the core collapses within seconds, heating up to 100 billion degree Kelvin. Huge amount of neutrons and neutrinos or created and the outer shell of the core accelerates inwards to more than 20% of the speed of light. However the degeneracy pressure of freshly created neutrons halts the implosion after a few seconds and the implosion bounces back, creating a outwards running shockwave, which blows the outer shells of the progenitor star in a cataclysmic explosion far into space. The neutrinos may also add substantial pressure to drive the shockwave outwards. The core itself might finally remain as a neutron star or collapse further into a black hole.
Swipe to see a wider field. Elliptical galaxy NGC 3377 on the bottom of this image is much closer. Its distance to earth is about 26 million light years.
Celestron RASA 11 v2
Celestron CGX-L mount
RisingCam ATR3CMOS26000KPA
UV/IR Cut filter
Bortle 4-5
No moon, high clouds
120x60sec (2h) UV/IR Cut Filter
PixInsight